Do you sometimes find yourself feeling like you’ve done everything right with your workout—have had water, stretched, and eaten properly—and wake up the following day feeling tired and sore? The answer may be as simple as this: insufficient sleep. Sleep is free, convenient, and effective ways of helping your body recover from exercise.
Good sleep not only leaves you feeling rested, but also allows your body to recover, become stronger, and prepare for the next exercise. In the following section, we will be outlining the ways sleep supports your body’s recovery and how you can track your sleep for better workout outcomes.
Why You Need to Sleep More After Exercise?
Does Sleep Make You Recover Quicker After Exercising? The answer is YES. Sleep helps you recover fast after exercise. When you exercise, especially you do hard workouts like lift weights, your muscles get small tears. But don’t worry, the tears are normal because they make your body strong. Your body will take time during this period to mend the tears, and sleep helps you with this.
Why Sleep Matters for Your Recovery After Exercise?
During sleep, your body starts healing itself. Your body repairs your muscle tissues and secretes growth hormones for your body to become stronger. According to research from National Library of Medicine, sleep not only helps the body replenish energy by restoring glycogen levels, but it also balances hormones like testosterone and growth hormone. Sleep also keeps your immune system healthy, just is like a reset button after tough training.
How Much Sleep Do You Actually Need?
So, just how much sleep does one really need? The answer is not one-size-fits-all—it varies by age. While babies and teenagers require much more sleep for growth and development, adults typically require 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night to function at their best.
Recommended
This sleep duration range is necessary for cognitive function, emotional stability, and overall health. Regularly lacking sleep can lead to sleep debt, which can impact everything from mood and memory to immune function and cardiovascular health.
How to Track and Improve Your Sleep?
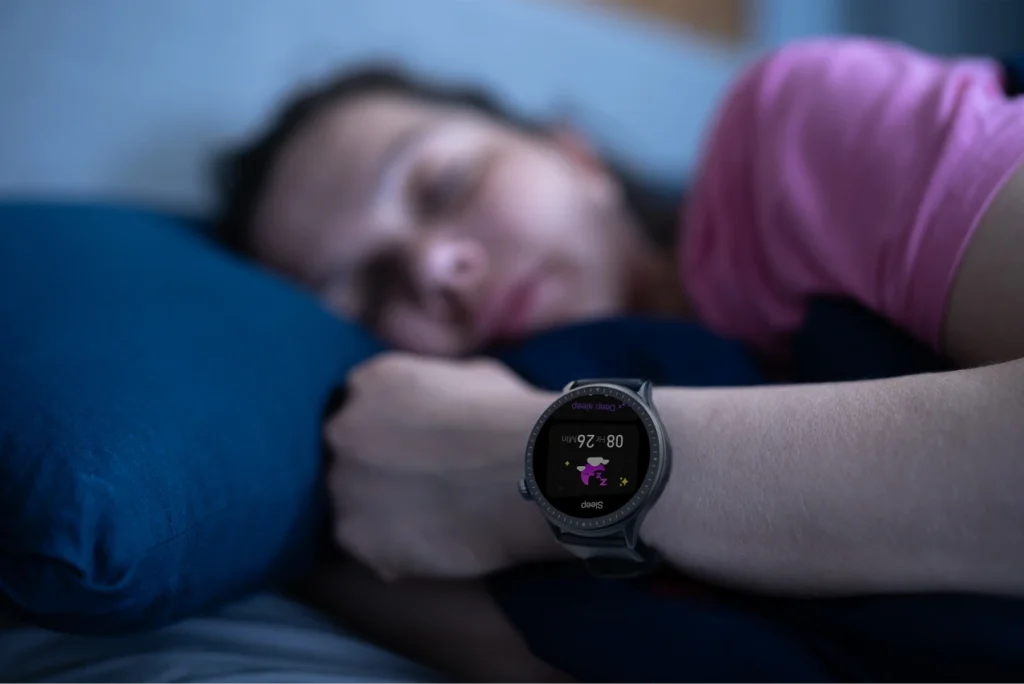
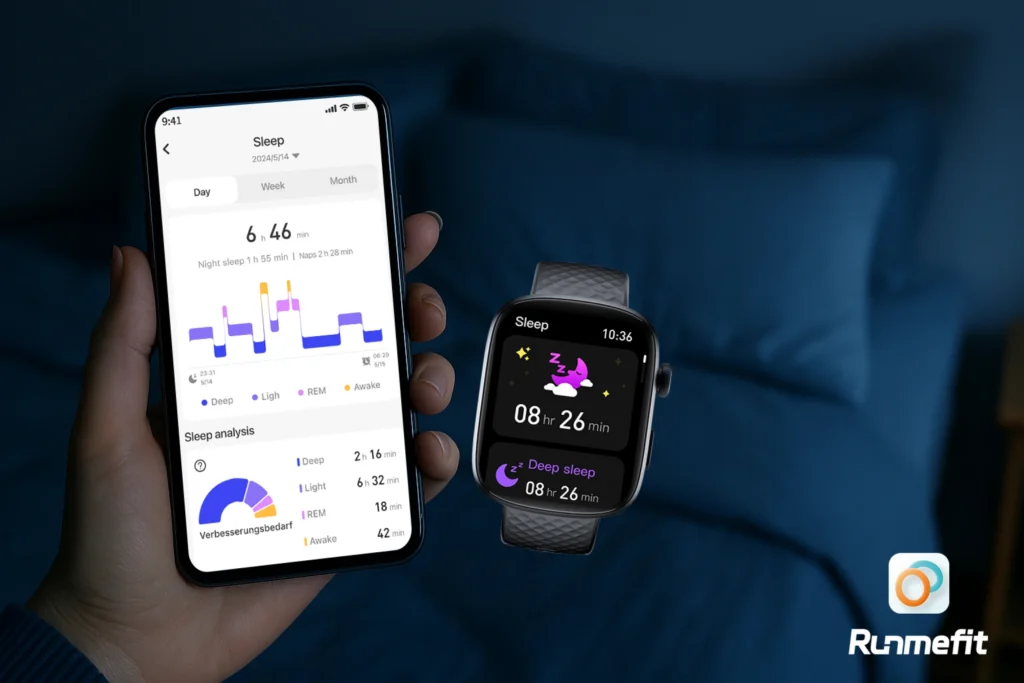
Knowing you sleep quality and sleep cycles can help you recover better. That’s why sleep monitoring is important. Tracking your sleep helps you better understand your sleep patterns and gain deeper insight into how much deep sleep and REM sleep you have. You can find easy tools for sleep monitoring with no effort.
Sleep Monitors
Sleep monitors or wearable devices, like the Runmefit watches, are great gadgets to track your sleep. They let you know the amount of sleep you have and the time spent on each stage, as well as the times you woke up. They provide detailed reports and sleep patterns over time, helping you clearly understand the effect of your habits, exercise, or stress on your sleep.
Recommended
1.43-inch AMOLED display, sleep phases tarcking, daily activity tracking, 24/7 heart rate monitoring, up to 15 days battery life
1.43-inch AMOLED display, sleep analysis & trends, built-in GPS, 60+ sports modes, swim modes, up to 15 days battery life
Once you know this, then some small adjustments can be made. You can, for example, go to sleep 30 minutes earlier, stop drinking caffeine after 2 pm, turn off screens at night. If you’re using a Runmefit smartwatch, then you will get valuable insights and will be able to make a customized sleep plan for better recovery.
Sleep Apps
There are so many sleep tracking apps available that function independently or with a watch. These apps collect you sleep data and display it in simply with scores, sleep stages, and long-term patterns.
Combined with the Runmefit app, you can use your Runmefit smartwatches or fitness trackers to customize sleep plan and keep track of your sleep phases and quality to get period trends and personalized tips. With its help, you can develop healthy sleeping habits, recover better from your workouts, and wake up refreshed.
Sleep Phases: What Happens in a Sleep Cycle?
Sleep is not one long period of unconsciousness—it is divided into stages. These cycles repeat, and each stage lasts approximately 90 minutes. Your body and brain achieve different things for each stage of sleep for the purpose of recovery.
The following represent the main stages of sleep:
Light Sleep
The first stage of falling asleep is light sleep. During this stage, your heart rate and breathing slow down, the body’s temperature drops, the muscles relax, and brain begins begins to suppress surrounding noise and other things. The body gets ready for deep sleep with this stage and you can wake up easily from this stage.
Light sleep usually lasts 10-25 minutes during the first sleep cycle. It accounts for half of your total sleeping time.
Deep Sleep
Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is very important for your body recovery. Your body will be busy repairing the muscles, creating new cells, and supporting the illmmune system. During this stage, our body also releases growth hormone for rebuilding the muscles and boosting the immune system. If you train heavily, most of the recovery will be during this period.
Deep sleep usually lasts 20-40 minutes. As the night goes on, this stage gets shorter and you spend more time in REM sleep.
REM Sleep
REM stands for Rapid Eye Movement. It’s an important stage for your brain and cognition recovery. Your brain is extremely active when you’re in REM sleep, and most of the dreaming is also done here. REM sleep is also responsible for learning, memory, cognition, and concentration. Your brain consolidates what you’ve learned during the day during this period.
REM sleep occurs approximately 90 minutes after we go to sleep. For most adults, it accounts for about 25% of the total sleeping time.
Which is More Important: Deep Sleep or REM Sleep?
Both stages are important, but each has special functions.
Deep sleep is for physical recovery—your body repairs, muscles rebuild, and tissues recover. It’s very important after hard workouts like strength training or long-distance running. If your body doesn’t get deep sleep, it will not be able to recover well.
REM sleep is more about mental recovery—it helps you stay focused, learn new skills, and balances your emotions. If you are learning a new sport or movement, REM sleep helps your brain remember it.
So, deep sleep is for your body, but REM sleep is for your brain. You need both of these for full recovery and improved training.
What If You Don't Get Enough Sleep?
Not getting enough sleep can slow down your fitness progress. Your body will take longer to recover and you may feel sore longer, and your performance will be below average. Poor sleep can also increase your risk of injury because your might feel less powerful or slower on your workout second day.
It can also make you feel stressed, moody, or tired. You might found yourself less motivated and less focused. In the long run, this can make your whole fitness plan harder to follow and even affect your hormones and immune system.
But if you sleep well, your strength and energy levels can be increased and you can also get better workout results. That’s why sleep is a key part of any fitness plan.
Tips for Better Sleep and Recovery
- Keep a regular sleep schedule each day.
- Make your room dark, cool, and peaceful.
- Stay away from screens and light.
- Don’t take big meals late at night.
- Don’t consume caffeine after the afternoon.
- Try light stretching or reading at night.
- Use a sleep tracker like Runmefit watch to understand your sleep patterns.
- Provide yourself with extra sleep after difficult workouts.
Sleep is more than just rest. It is a vital part of body and mind rejuvenation. If sleep is part of your training program, you will feel better, recover faster, and perform at your best.

























